With Cranium, our physical property estimation software package, you can:
- generate estimates by simply drawing your chemical's molecular structure or entering your mixture's composition
- estimate values for more than 30 physical properties including constant properties, solubilities, safety properties, environmental properties, temperature and pressure dependent properties and phase equilibria
- create a database to manage the physical property data for all your important chemicals and formulations
- tailor Cranium's estimation strategy by entering rules on each estimation technique
- easily add your own, estimation technique capturing and retaining your company's hard earned proprietary physical property knowledge
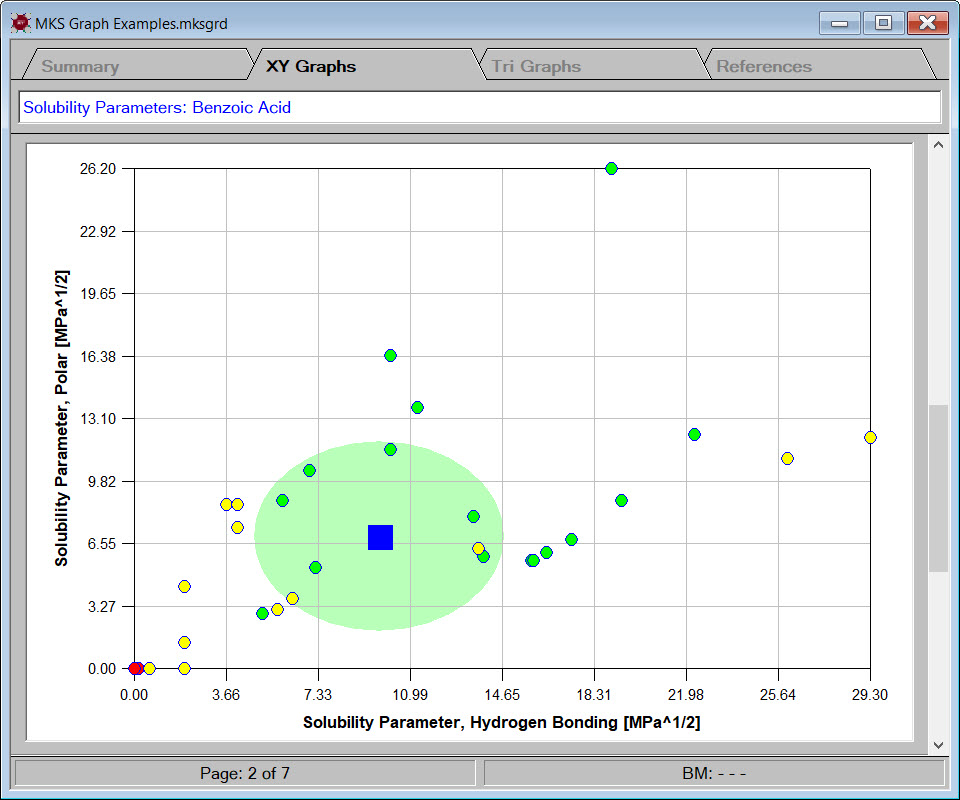
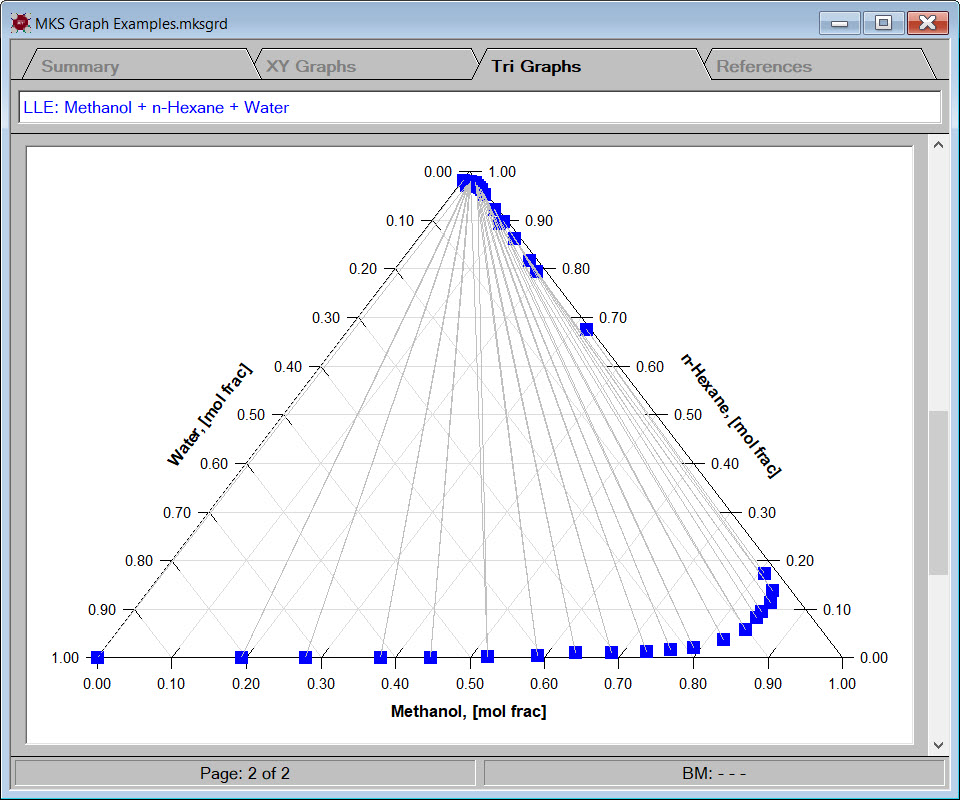
- generate graphs to compare physical properties estimated by different techniques or for general analysis and presentation
- export physical property values to process simulators, spreadsheets, and other chemical software
For more details, please read through our Cranium brochure, view our YouTube videos and, most importantly, experiment with the Cranium demonstration version.
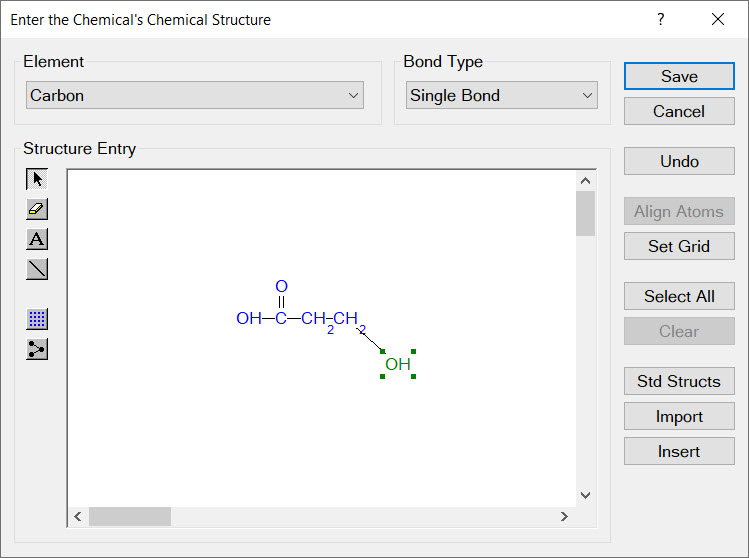
To estimate the physical properties of a new chemical, you simply need to draw the chemical's molecular structure and issue Cranium's Estimate Properties command. Cranium will use a set of Applicability and Accuracy rules to select the best estimation technique for more than 30 physical properties. You can also import molecular structures into Cranium from popular chemistry software tools.
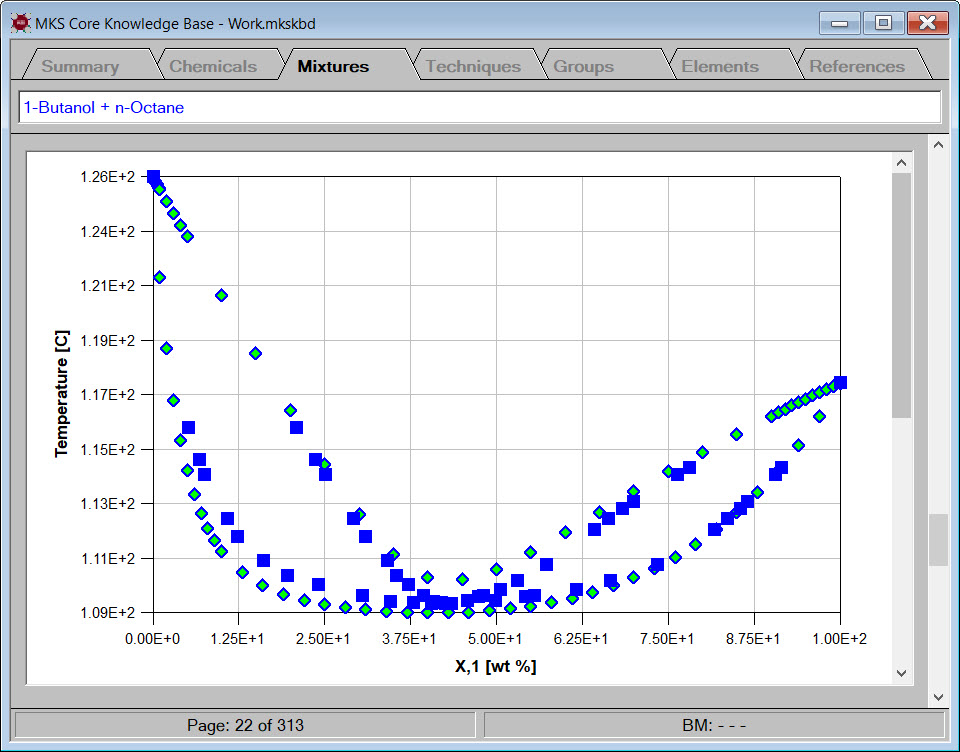
To estimate the physical properties of a new mixture, you simply need to enter the chemical components and compositions. You may use units of mole fraction, mole percent, weight fraction and weight percent. Cranium will perform all concentration conversions before estimating the mixture's physical properties.
Certain estimation techniques require the input of physical properties. For example, many vapor pressure estimation techniques require the input of boiling point, critical temperature and critical pressure. If data values are not available for these properties, Cranium will recursively estimate them again choosing the best estimation technique for each property.
For more details:
- experiment with our Cranium demonstration version
- read through our Cranium brochure
- view our YouTube videos
| Some of the Physical Properties Estimated by Cranium | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acentric Factor | Activity Coefficient | Aquatic Toxicity | Autoignition Temperature | Boiling Point |
| Bubble Point | Critical Pressure | Critical Temperature | Critical Volume | Densities |
| Diffusion Coefficients | Dew Point | Enthalpy of Formation | Enthalpy of Fusion | Enthalpy of Vaporization |
| Flash Point | Freezing Point | Fugacity Coefficient | Gibbs Energy of Formation | Heat Capacities |
| Henry's Constant | Lower Flammability Limit | Melting Point | Molecular Weight | Octanol-Water Partition |
| Refractive Index | Relative Permittivity | Solubility Parameter | Speed of Sound | Surface Tension |
| Thermal Conductivities | Upper Flammability Limit | Vapor Pressure | Viscosities | Water Solubility |
We are continually evaluating and adding new estimation techniques:
- we first compile the data needed to evaluate a new technique
- we code the technique into a knowledge base document using Cranium's simple input language
- we use the analysis tools within Cranium to determine the applicability and accuracy of the technique
- we finally post the updated knowledge base on our website where our users can download the new data and new technique
| Property | Estimation Technique |
|---|---|
| Acentric Factor | AcF: Definition [MKS] |
| Acentric Factor | AcF: Lee + Kesler Relation [MKS] |
| Activity Coefficient, LLE - f(T,P,X) | ActC,LLE (T,P,X): UNIFAC Method [MKS] |
| Activity Coefficient, VLE - f(T,P,X) | ActC,VLE (T,P,X): DECHEMA, Margules - 500 mmHg [MKS] |
| Activity Coefficient, VLE - f(T,P,X) | ActC,VLE (T,P,X): Holmes + van Winkle, Margules - 500 mmHg [MKS] |
| Activity Coefficient, VLE - f(T,P,X) | ActC,VLE (T,P,X): Holmes + van Winkle, Margules - 760 mmHg [MKS] |
| Activity Coefficient, VLE - f(T,P,X) | ActC,VLE (T,P,X): Holmes + van Winkle, van Laar - 500 mmHg [MKS 01] |
| Activity Coefficient, VLE - f(T,P,X) | ActC,VLE (T,P,X): Holmes + van Winkle, van Laar - 760 mmHg [MKS] |
| Activity Coefficient, VLE - f(T,P,X) | ActC,VLE (T,P,X): Holmes + van Winkle, Wilson - 760 mmHg [MKS] |
| Activity Coefficient, VLE - f(T,P,X) | ActC,VLE (T,P,X): Modified UNIFAC (Dortmund) Method [MKS] |
| Activity Coefficient, VLE - f(T,P,X) | ActC,VLE (T,P,X): MOSCED [MKS] |
| Activity Coefficient, VLE - f(T,P,X) | ActC,VLE (T,P,X): UNIFAC Method [MKS] |
| Autoignition Temperature | AIT: Chen + Liaw + Kuo Method [MKS] |
| Boiling Point | Tb: Antoine Equation - PGL 2001 [MKS] |
| Boiling Point | Tb: Joback Method [MKS] |
| Boiling Point | Tb: Stein + Brown Method [MKS] |
| Boiling Point - f(X) | Tb (X): Gamma-Ideal Method [MKS] |
| Critical Compressibility | Zc: Definition [MKS] |
| Critical Pressure | Pc: Joback Method [MKS] |
| Critical Pressure | Pc: Lydersen Method [MKS] |
| Critical Pressure | Pc: Myers + Danner Technique [MKS] |
| Critical Pressure | Pc: Vapor Pressure Extrapolation [MKS] |
| Critical Pressure | Pc: Wilson + Jasperson Method [MKS] |
| Critical Pressure - f(X) | Pc (X): Chueh + Prausnitz Method [MKS] |
| Critical Pressure - f(X) | Pc (X): Kreglewski + Kay Method [MKS] |
| Critical Temperature | Tc: Fedors Technique [MKS] |
| Critical Temperature | Tc: Joback Method [MKS] |
| Critical Temperature | Tc: Klincewicz Method [MKS] |
| Critical Temperature | Tc: Lydersen Method [MKS] |
| Critical Temperature | Tc: Myers + Danner Technique [MKS] |
| Critical Temperature | Tc: Tu Method [MKS] |
| Critical Temperature | Tc: Wilson + Jasperson Method - First Order [MKS] |
| Critical Temperature - f(X) | Tc (X): Chueh + Prausnitz Method [MKS] |
| Critical Temperature - f(X) | Tc (X): Li Technique [MKS] |
| Critical Volume | Vc: Ambrose Method [MKS] |
| Critical Volume | Vc: Joback Method [MKS] |
| Critical Volume | Vc: Lydersen Method [MKS] |
| Critical Volume - f(X) | Vc (X): Chueh + Prausnitz Method [MKS] |
| Critical Volume - f(X) | Vc (X): Li + Kiran + Lydersen Method [MKS] |
| Density, Liquid - f(T) | Den,l (T): Bhirud Technique [MKS] |
| Density, Liquid - f(T) | Den,l (T): Dippr Equation 105 [MKS] |
| Density, Liquid - f(T) | Den,l (T): GCVol Method [MKS] |
| Density, Liquid - f(T) | Den,l (T): Hankinson + Thomson [MKS] |
| Density, Liquid - f(T) | Den,l (T): IAPWS Formula 1995 [MKS] |
| Density, Liquid - f(T) | Den,l (T): Modified Rackett Equation [MKS] |
| Density, Liquid - f(T) | Den,l (T): Peng + Robinson EOS [MKS] |
| Density, Liquid - f(T) | Den,l (T): Rackett Equation [MKS] |
| Density, Liquid - f(T) | Den,l (T): Redlich + Kwong EOS [MKS] |
| Density, Liquid - f(T) | Den,l (T): Soave + Redlich + Kwong EOS [MKS] |
| Density, Liquid - f(T) | Den,l (T): van der Waals EOS [MKS] |
| Density, Liquid - f(T,P) | Den,l (T,P): Peng + Robinson EOS [MKS] |
| Density, Liquid - f(T,P) | Den,l (T,P): Redlich + Kwong EOS [MKS] |
| Density, Liquid - f(T,P) | Den,l (T,P): Soave + Redlich + Kwong EOS [MKS] |
| Density, Liquid - f(T,P) | Den,l (T,P): Thomas + Brobst + Hankinson Method [MKS] |
| Density, Liquid - f(T,P) | Den,l (T,P): van der Waals EOS [MKS] |
| Density, Liquid - f(T,P,X) | Den,l (T,P,X): Peng + Robinson EOS [MKS] |
| Density, Liquid - f(T,P,X) | Den,l (T,P,X): Soave + Redlich + Kwong EOS [MKS] |
| Density, Liquid - f(T,X) | Den,l (T,X): Hankinson + Thomson [MKS] |
| Density, Liquid - f(T,X) | Den,l (T,X): Spencer + Danner Method [MKS] |
| Density, Vapor - f(T,P) | Den,v (T,P): Ideal Gas Law [MKS] |
| Density, Vapor - f(T,P) | Den,v (T,P): Peng + Robinson EOS [MKS] |
| Density, Vapor - f(T,P) | Den,v (T,P): Redlich + Kwong EOS [MKS] |
| Density, Vapor - f(T,P) | Den,v (T,P): Soave + Redlich + Kwong EOS [MKS] |
| Density, Vapor - f(T,P) | Den,v (T,P): van der Waals EOS [MKS] |
| Density, Vapor - f(T,P,X) | Den,v (T,P,X): Peng + Robinson EOS [MKS] |
| Density, Vapor - f(T,P,X) | Den,v (T,P,X): Soave + Redlich + Kwong EOS [MKS] |
| Diffusion Coefficient, Vapor - f(T,P,X) | DiffC,v (T,P,X): Chapman + Enskog Method [MKS] |
| Enthalpy of Combustion at 298K | Hc,298: Enthalpy Difference Calculation [MKS] |
| Enthalpy of Formation, Liquid at 298K | Hf,l,298: Vapor Estimate Adjustment [MKS] |
| Enthalpy of Formation, Vapor at 298K | Hf,v,298: Joback Method [MKS] |
| Enthalpy of Fusion at Tm | Hm,tm: Joback Method [MKS] |
| Enthalpy of Vaporization - f(T) | Hv (T): Dippr Equation 106 [MKS] |
| Enthalpy of Vaporization - f(T) | Hv (T): Pitzer Correlation [MKS] |
| Enthalpy of Vaporization - f(T) | Hv (T): Tu + Liu Method [MKS] |
| Enthalpy of Vaporization - f(T) | Hv (T): Watson Relation [MKS] |
| Enthalpy of Vaporization at Tb | Hv,tb: Chen Method [MKS] |
| Enthalpy of Vaporization at Tb | Hv,tb: Joback Method [MKS] |
| Enthalpy of Vaporization at Tb | Hv,tb: Riedel Method [MKS] |
| Enthalpy of Vaporization at Tb | Hv,tb: Vetere Method [MKS] |
| Enthalpy, Liquid - f(T) | H,l (T): Trapezoid Integration Method [MKS] |
| Enthalpy, Liquid - f(T,P) | H,l (T,P): Trapezoid Integration Method [MKS] |
| Enthalpy, Vapor - f(T) | H,v (T): Trapezoid Integration Method [MKS] |
| Entropy, Liquid - f(T) | S,l (T): Trapezoid Integration Method [MKS] |
| Entropy, Vapor - f(T) | S,v (T): Trapezoid Integration Method [MKS] |
| Flammability Limit, Lower | LFL: Seaton Method [MKS] |
| Flammability Limit, Lower | LFL: Shebeko Atom Technique [MKS] |
| Flammability Limit, Lower | LFL: Shebeko Modified Technique [MKS] |
| Flammability Limit, Lower - f(X) | LFL (X): Le Chatelier Method [MKS] |
| Flammability Limit, Upper | UFL: High + Danner Method [MKS] |
| Flammability Limit, Upper | UFL: Seaton Method [MKS] |
| Flammability Limit, Upper - f(X) | UFL (X): Le Chatelier Method [MKS] |
| Flash Point, Closed Cup | Tf,cc: Affens Method [MKS] |
| Flash Point, Closed Cup | Tf,cc: Butler + Cooke + Lukk + Jameson Method [MKS] |
| Flash Point, Closed Cup | Tf,cc: Catoire + Naudet Method [MKS] |
| Flash Point, Closed Cup | Tf,cc: Hshieh Organics Method [MKS] |
| Flash Point, Closed Cup | Tf,cc: Patil Method [MKS] |
| Flash Point, Closed Cup | Tf,cc: Satyanarayana + Kakati Method [MKS] |
| Flash Point, Closed Cup - f(X) | Tf,cc (X): Catoire + Paulmier + Naudet Ideal Method [MKS] |
| Flash Point, Closed Cup - f(X) | Tf,cc (X): Catoire + Paulmier + Naudet Method [MKS] |
| Flash Point, Closed Cup - f(X) | Tf,cc (X): Liaw + Tang + Lai Method [MKS] |
| Fugacity Coefficient, Liquid - f(T,P) | Fug,l (T,P): Peng + Robinson EOS [MKS] |
| Fugacity Coefficient, Liquid - f(T,P,X) | Fug,l (T,P,X): Peng + Robinson EOS [MKS] |
| Fugacity Coefficient, Vapor - f(T,P) | Fug,v (T,P): Peng + Robinson EOS [MKS] |
| Fugacity Coefficient, Vapor - f(T,P,X) | Fug,v (T,P,X): Peng + Robinson EOS [MKS] |
| General Calculation | GenCalc: 2-Hydroxybenzoic acid solubility at 25°C [MKS] |
| General Calculation | GenCalc: Diffusion in Air (25C, 101kPa, cm2/sec) [MKS] |
| General Calculation | GenCalc: Hill Cross Sectional Area - [MKS] |
| General Calculation | GenCalc: Naphthalene solubility at 25°C [MKS] |
| General Calculation | GenCalc: Number of Oxygen Atoms [MKS] |
| General Calculation | GenCalc: Oxygen Balance Calculation [MKS] |
| General Calculation | GenCalc: Solubility in pyridine at 25°C [MKS] |
| General Calculation | GenCalc: Specific Gravity at 20°C [MKS] |
| General Calculation - f(X) | GenCalc (X): Binary Azeotrope Formed [MKS] |
| General Calculation - f(X) | GenCalc (X): Percentage of Wetted Surface Area - [MKS] |
| Gibbs Energy of Formation, Vapor at 298K | Gf,v,298: Joback Method [MKS] |
| Heat Capacity - Isobaric, Liquid - f(T) | Cp,l (T): Dippr Equation 100 [MKS] |
| Heat Capacity - Isobaric, Liquid - f(T) | Cp,l (T): IUPAC Cubic Splines [MKS] |
| Heat Capacity - Isobaric, Liquid - f(T) | Cp,l (T): Missenard Method [MKS] |
| Heat Capacity - Isobaric, Liquid - f(T) | Cp,l (T): Poling + Prausnitz + O'Connell CSP Method [MKS] |
| Heat Capacity - Isobaric, Liquid - f(T,X) | Cp,l (T,X): Ideal Molar Mixing Rule [MKS] |
| Heat Capacity - Isobaric, Liquid at 298K | Cp,l,298: Chickos + Acree Method [MKS] |
| Heat Capacity - Isobaric, Solid - f(T) | Cp,s (T): Goodman + Wilding + Oscarson + Rowley Method [MKS] |
| Heat Capacity - Isobaric, Solid at 298K | Cp,s,298: Chickos + Acree Method [MKS] |
| Heat Capacity - Isobaric, Solid at 298K | Cp,s,298: Hurst + Harrison [MKS] |
| Heat Capacity - Isobaric, Vapor - f(T) | Cp,v (T): Dippr Equation 107 [MKS] |
| Heat Capacity - Isobaric, Vapor - f(T) | Cp,v (T): Joback Method [MKS] |
| Heat Capacity - Isobaric, Vapor - f(T,X) | Cp,v (T,X): Ideal Molar Mixing Rule [MKS] |
| Heat Capacity - Isobaric, Vapor at 298K | Cp,v,298: Fixed Temperature Method [MKS] |
| Heat Capacity - Isobaric, Vapor at 298K | Cp,v,298: Joback Method [MKS] |
| Heat Capacity - Isometric, Vapor - f(T) | Cv,v (T): Ideal Gas Relation [MKS] |
| Henry's Constant (pc) in H2O - f(T) | Hpc (T): Penttilä + Dell'Era + Uusi-Kyyny + Alopaeus Method [MKS] |
| Henry's Constant (px) in H2O - f(T) | Hpx (T): Carroll + Slupsky + Mather Method [MKS] |
| Henry's Constant (px) in H2O - f(T) | Hpx (T): Fernández-Prini + Alvarez + Harvey Method [MKS] |
| LC50 96hr, Fathead Minnow | LC50,96hr,FatMn: Martin + Young Method [MKS] |
| log(Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient) | log P: Lin + Sandler Method [MKS] |
| Melting Point | Tm: Constantinou + Gani First Order Method [MKS] |
| Melting Point | Tm: Joback Method [MKS] |
| Molecular Weight | Mw: Definition [MKS] |
| Molecular Weight - f(X) | Mw (X): Definition [MKS] |
| Refractive Index, Liquid at 293K | RI,l: Lorentz + Lorenz Equation [MKS] |
| SLE, Liquidus Temperature - f(P,X) | LiqPtTmp (P,X): Gamma VLE Eutectic Method [MKS] |
| SLE, Liquidus Temperature - f(P,X) | LiqPtTmp (P,X): Ideal Eutectic Model [MKS] |
| Solubility Parameter, Dispersive | SP,d: Stefanis + Panayiotou Method, First Order [MKS] |
| Solubility Parameter, Dispersive - f(X) | SP,d (X): Ideal Volume Fraction Average [MKS] |
| Solubility Parameter, Hydrogen Bonding | SP,h: Stefanis + Panayiotou Method, First Order - Std [MKS] |
| Solubility Parameter, Hydrogen Bonding - f(X) | SP,h (X): Ideal Volume Fraction Average [MKS] |
| Solubility Parameter, Polar | SP,p: Hansen + Beerbower Method [MKS] |
| Solubility Parameter, Polar | SP,p: Stefanis + Panayiotou Method, First Order - Std [MKS] |
| Solubility Parameter, Polar - f(X) | SP,p (X): Ideal Volume Fraction Average [MKS] |
| Solubility Parameter, Total | SP,t: Definition [MKS] |
| Solubility Parameter, Total | SP,t: Fedors Technique [MKS] |
| Solubility Parameter, Total | SP,t: Three Term Definition - Data [MKS] |
| Solubility Parameter, Total | SP,t: Three Term Definition [MKS] |
| Speed of Sound, Liquid - f(T) | SpSnd,l (T): Peng + Robinson EOS [MKS] |
| Speed of Sound, Vapor - f(T,P) | SpSnd,v (T,P): Peng + Robinson EOS [MKS] |
| Surface Tension, Liquid - f(T) | SurfTn,l (T): Brock + Bird Method [MKS] |
| Surface Tension, Liquid - f(T) | SurfTn,l (T): Dippr Equation 106 [MKS] |
| Surface Tension, Liquid - f(T) | SurfTn,l (T): Sastri + Rao Method [MKS] |
| Surface Tension, Liquid - f(T) | SurfTn,l (T): Somayajulu [MKS] |
| Surface Tension, Liquid - f(T,X) | SurfTn,l (T,X): Molar Average [MKS] |
| Thermal Conductivity, Liquid - f(T) | ThrmCnd,l (T): Dippr Equation 100 [MKS] |
| Thermal Conductivity, Liquid - f(T) | ThrmCnd,l (T): Mallan + Michaelian + Lockhart Method [MKS] |
| Thermal Conductivity, Liquid - f(T) | ThrmCnd,l (T): Missenard + Riedel Method [MKS] |
| Thermal Conductivity, Liquid - f(T) | ThrmCnd,l (T): Sastri + Rao Method [MKS] |
| Thermal Conductivity, Liquid - f(T) | ThrmCnd,l (T): Sato + Riedel Method [MKS] |
| Thermal Conductivity, Liquid - f(T,X) | ThrmCnd,l (T,X): Filippov Equation [MKS] |
| Thermal Conductivity, Liquid - f(T,X) | ThrmCnd,l (T,X): Jamieson + Irving + Tudhope Correlation [MKS] |
| Thermal Conductivity, Liquid - f(T,X) | ThrmCnd,l (T,X): Power Law Relation [MKS] |
| Thermal Conductivity, Vapor - f(T) | ThrmCnd,v (T): Dippr Equation 102 [MKS] |
| Thermal Conductivity, Vapor - f(T) | ThrmCnd,v (T): Eucken Correlation [MKS] |
| Thermal Conductivity, Vapor - f(T) | ThrmCnd,v (T): Modified Eucken Correlation [MKS] |
| Thermal Conductivity, Vapor - f(T) | ThrmCnd,v (T): Stiel + Thodos Method [MKS] |
| Thermal Conductivity, Vapor - f(T,P) | ThrmCnd,v (T,P): Stiel + Thodos High Pressure Method [MKS] |
| Triple Point, Pressure | TrpPtPrs: Liquid Vapor Pressure Method [MKS] |
| Triple Point, Pressure | TrpPtPrs: Solid Vapor Pressure Method [MKS] |
| Triple Point, Temperature | TrpPtTmp: Melting Point Technique |
| Vapor Pressure, Liquid - f(T) | Pvp,l (T): Ambrose + Walton Method [MKS] |
| Vapor Pressure, Liquid - f(T) | Pvp,l (T): Antoine Equation - PGL 2001 [MKS] |
| Vapor Pressure, Liquid - f(T) | Pvp,l (T): Dippr Equation 101 [MKS] |
| Vapor Pressure, Liquid - f(T) | Pvp,l (T): Gómez-Nieto + Thodos Equation [MKS] |
| Vapor Pressure, Liquid - f(T) | Pvp,l (T): IAPWS Formula 1995 [MKS] |
| Vapor Pressure, Liquid - f(T) | Pvp,l (T): Lee + Kesler Equation [MKS] |
| Vapor Pressure, Liquid - f(T) | Pvp,l (T): Riedel + Plank + Miller Equation [MKS] |
| Vapor Pressure, Solid - f(T) | Pvp,s (T): Jones Method [MKS] |
| Viscosity, Liquid - f(T) | Visc,l (T): Dippr Equation 101 [MKS] |
| Viscosity, Liquid - f(T) | Visc,l (T): Joback Method [MKS] |
| Viscosity, Liquid - f(T) | Visc,l (T): Orrick + Erbar Method [MKS] |
| Viscosity, Liquid - f(T) | Visc,l (T): Przezdziecki + Sridhar Method [MKS] |
| Viscosity, Liquid - f(T,P) | Visc,l (T,P): Lucas Method [MKS] |
| Viscosity, Liquid - f(T,X) | Visc,l (T,X): Arrhenius Equation [MKS] |
| Viscosity, Liquid - f(T,X) | Visc,l (T,X): Kendall + Monroe Relation [MKS] |
| Viscosity, Vapor - f(T) | Visc,v (T): Dippr Equation 102 [MKS] |
| Viscosity, Vapor - f(T) | Visc,v (T): Lucas Method [MKS] |
| Viscosity, Vapor - f(T) | Visc,v (T): Reichenberg Technique [MKS] |
| Viscosity, Vapor - f(T) | Visc,v (T): Yoon + Thodos Method [MKS] |
| Viscosity, Vapor - f(T,P) | Visc,v (T,P): Reichenberg Method [MKS] |
| Viscosity, Vapor - f(T,X) | Visc,v (T,X): Wilke Equation [MKS] |
| VLE, Bubble Pressure - f(T,X) | BubPtPrs (T,X): Gamma-Ideal Method [MKS] |
| VLE, Bubble Pressure - f(T,X) | BubPtPrs (T,X): Ideal-Ideal Method [MKS] |
| VLE, Bubble Pressure - f(T,X) | BubPtPrs (T,X): Phi-Phi Method [MKS] |
| VLE, Bubble Temperature - f(P,X) | BubPtTmp (P,X): Gamma-Ideal Method [MKS] |
| VLE, Bubble Temperature - f(P,X) | BubPtTmp (P,X): Ideal-Ideal Method [MKS] |
| VLE, Bubble Temperature - f(P,X) | BubPtTmp (P,X): Phi-Phi Method [MKS] |
| VLE, Dew Pressure - f(T,X) | DewPtPrs (T,X): Gamma-Ideal Method [MKS] |
| VLE, Dew Pressure - f(T,X) | DewPtPrs (T,X): Ideal-Ideal Method [MKS] |
| VLE, Dew Pressure - f(T,X) | DewPtPrs (T,X): Phi-Phi Method [MKS] |
| VLE, Dew Temperature - f(P,X) | DewPtTmp (P,X): Gamma-Ideal Method [MKS] |
| VLE, Dew Temperature - f(P,X) | DewPtTmp (P,X): Ideal-Ideal Method [MKS] |
| VLE, Dew Temperature - f(P,X) | DewPtTmp (P,X): Phi-Phi Method [MKS] |
Once you have entered data and generated estimates, you can export these physical property values to a number of process simulators, analysis tools and other chemicals software products:
| ASPEN Input File | CHEMCAD Neutral File |
| Chemical Structure Images | DIPPR Database Format |
| MATLAB Class Definition | MKS JSON File Format |
| Mol File Format | ProSim Simulis Format |
| SD File Format | AVEVA SimCentral Format |
| ioMosaic SuperChems File | UniSim File Format |
- Download and experiment with our Cranium demonstration version
- Download and install Cranium Version 4.2 (license required)
- Follow a step-by-step physical property estimation example
- Download and read through our Cranium brochure
- View one of our YouTube videos
- Install a previous version