The Stein + Brown boiling point method is a group contribution technique applicable to a broad range of organic chemicals. The technique is very easy to use - there is a single set of group contributions, no corrections for rings and no group interactions. A final "adjustment" calculation improves the boiling point estimates of higher molecular weight chemicals.
As with all group contribution techniques, the steps for generating an estimate are:
- dissect the chemical's structure into groups (see code lines 017 through 019)
- total the contributions for each group (see code lines 021 through 038)
- insert this contribution total into the model's equation (see code lines 040 and 041).
The final adjustment of the estimate is performed in code lines 043 through 048.
References:
- S. E. Stein and R. L. Brown. "Estimation of Normal Boiling Points from Group Contributions." Journal of Chemical Information and Computer Science. Volume 34, number 3, page 581-587, 1994. (View on publisher's site)
This example estimates the normal boiling point of 3-isopropyl-6-methylene-1-cyclohexene. (Note that the estimation technique distinguishes between acyclic groups and ring groups having the same molecular structure.)
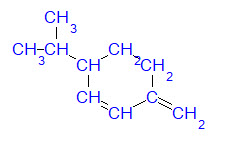
Dissecting this molecular structure into the technique's groups gives the occurrences shown in the table to the right. Multiplying each group's occurrence by its contribution gives the subtotals shown in the table. Adding these subtotals together gives the total shown at the bottom of the table.
Inserting the total of the contributions into the model shown at the top of the page gives an estimate of 431.76K. This is in very good agreement with the reported experimental value of 447.15K.
| Example Calculations | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Group | Count | Contribution | Subtotal |
| [*]=C-[*]2 (ss) | 1 | 28.19 | 28.19 |
| [*]=CH-[*] (ds) | 2 | 28.03 | 56.06 |
| [*]=CH2 | 1 | 16.44 | 16.44 |
| [*]2-CH-[*] | 1 | 11.86 | 11.86 |
| [*]2-CH-[*] (ss) | 1 | 21.66 | 21.66 |
| [*]-CH2-[*] (ss) | 2 | 26.44 | 52.88 |
| [*]-CH3 | 2 | 21.98 | 43.96 |
| Total | - - - | - - - | 231.05 |
| Example Results | |
|---|---|
| Estimated Value | 445.75 K |
| Literature Value | 447.15 K |
The figure to the right shows that the estimation technique's errors are fairly consistent, i.e., errors do not depend upon the value of the estimated boiling point.
This evaluation was performed on January 30, 2023 using Cranium, Professional Edition version 5.0.
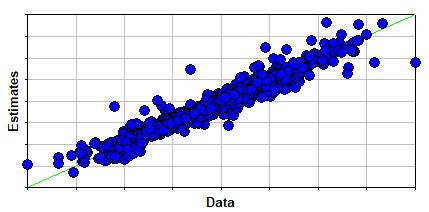
| Summary Statistics | ||
|---|---|---|
| Statistic | Value | Units |
| # Observations | 1429 | - - - |
| Avg Abs % Error | 3.7422 | % |
| Max Abs % Error | 115.79 | % |
| Min Abs % Error | 0.0174 | % |
| Avg Abs Error | 14.918 | K |
| Max Abs Error | 207.5 | K |
| Min Abs Error | 0.071706 | K |
| Avg Error | -0.47781 | K |
| Max Error | 197.99 | K |
| Min Error | -207.5 | K |
| Example Estimation Errors | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical | Data [K] | Estimates [K] | % Error |
| (±)-1-Phenylethanol | 477.15 | 480.21 | 0.641 |
| 1,1,2,2-Tetrachlorodifluoroethane | 366.00 | 353.93 | -3.298 |
| 1,2-Dichlorobenzene | 453.57 | 447.79 | -1.274 |
| 1-Octanol | 468.35 | 473.78 | 1.159 |
| 2-Butyne | 300.13 | 311.90 | 3.922 |
| Acrylonitrile | 350.50 | 367.75 | 4.922 |
| Benzaldehyde | 451.90 | 454.32 | 0.536 |
| Benzene | 353.25 | 375.34 | 6.253 |
| Bromobenzene | 429.24 | 435.52 | 1.463 |
| Cyclohexanol | 434.00 | 457.18 | 5.341 |
| Cyclohexanone | 428.90 | 428.08 | -0.191 |
| Ethanethiol | 308.15 | 331.12 | 7.454 |
| Ethyl acetate | 350.30 | 351.01 | 0.203 |
| Ethyl thioacetate | 388.00 | 411.74 | 6.119 |
| Hexamethyldisiloxane | 372.55 | 377.59 | 1.353 |
| Isopropylbenzene | 425.56 | 430.13 | 1.074 |
| Methyl salicylate | 493.65 | 525.30 | 6.411 |
| n-Decanoic acid | 543.15 | 551.87 | 1.605 |
| n-Heptanoic acid | 496.15 | 499.97 | 0.770 |
| Oxazole | 342.65 | 364.80 | 6.464 |
| o-Xylene | 417.58 | 421.40 | 0.915 |
| Styrene | 418.31 | 419.75 | 0.344 |
| Succinic acid | 591.00 | 553.53 | -6.340 |
| Tetrahydrofuran | 338.00 | 342.45 | 1.317 |
| Tetrahydrothiophene | 394.27 | 378.87 | -3.906 |
| Toluene | 383.78 | 398.82 | 3.919 |
| γ-Butyrolactone | 478.15 | 450.04 | -5.879 |
We continue to analyze estimation results to develop additional accuracy rules for Cranium and Synapse. The current rules are shown in the code to the right. (Note that the error value used in the rule was determined after several outliers were removed from the analysis.)
| Group Occurrences | |
|---|---|
| Group | Occurence |
The structure entered above is added to a property estimation request which is sent to an instance of our Cranium, Web Server Edition software product running on a Microsoft Azure virtual machine. Cranium processes the request - dissecting the structure into groups and estimating physical properties. These resulting values are then sent back to this webpage for display.
Click here to learn more about how you can use our Cranium Web Server to distribute your company's physical property data, estimates, and knowledge throughout your organization or contact us for further details.
- Follow a step-by-step physical property estimation example
- Download and experiment with our Cranium Basic Edition
- Download and experiment with our Synapse Basic Edition
- Download and read through our Cranium brochure
- Download and read through our Synapse brochure
- View one of our demonstration videos